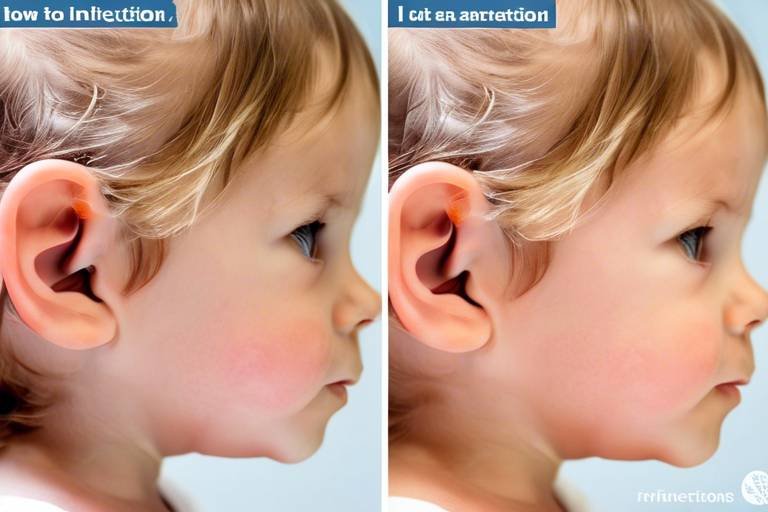
How to Identify and Treat Ear Infections
This article explores the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for ear infections, providing essential information for understanding and managing this common condition effectively.
Ear infections occur when bacteria or viruses invade the middle ear, leading to inflammation and discomfort. Recognizing the types of ear infections is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. There are primarily three types of ear infections: acute otitis media, which is a sudden onset of infection; otitis media with effusion, where fluid remains in the ear after an infection; and chronic otitis media, which is a persistent infection. Each type presents unique challenges and requires tailored approaches for management.
Identifying the symptoms of ear infections is vital for timely intervention. Symptoms can vary by age and may include pain, fever, and irritability in children, while adults may experience hearing loss and drainage. Understanding these symptoms can significantly impact the speed and effectiveness of treatment. For instance, if a child is tugging at their ear or seems unusually fussy, it may indicate discomfort due to an ear infection.
Children often exhibit specific signs of ear infections, such as tugging at the ear, fussiness, and difficulty sleeping. They may also have a fever and exhibit a loss of appetite. Early detection is essential to prevent complications and ensure prompt treatment. If a child shows these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider to assess the situation accurately.
In adults, ear infections may manifest through ear pain, fluid drainage, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. Some might also experience dizziness or balance issues, which can be quite alarming. Recognizing these symptoms can lead to quicker medical attention, preventing further complications. If you notice these signs, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for an evaluation.
Understanding the causes of ear infections helps in prevention and management. Common triggers include allergies, colds, and sinus infections, which can lead to fluid buildup in the ear. When the Eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the back of the throat, become blocked or swollen, it can create an environment ripe for infection. This blockage can be due to various reasons, including environmental factors and underlying health issues.
Allergies can cause inflammation in the nasal passages, leading to fluid accumulation in the ears. This fluid can become infected, resulting in an ear infection that requires medical attention. It’s essential to manage allergies effectively to reduce the risk of developing ear infections, especially in children who are more susceptible.
Upper respiratory infections, such as colds or flu, are often precursors to ear infections. They can cause swelling and blockage of the Eustachian tubes, leading to fluid retention and infection. If you find yourself frequently battling colds, consider preventive measures to strengthen your immune system and reduce the likelihood of subsequent ear infections.
Effective treatment for ear infections may include antibiotics, pain relievers, and home remedies. Understanding these options can help in choosing the best course of action for recovery. It’s important to note that not all ear infections require antibiotics; many can resolve on their own, especially viral infections. Consulting with a healthcare provider is key to determining the appropriate treatment.
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed for bacterial ear infections, while over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort. It's essential to follow medical advice for optimal recovery. Misuse of antibiotics can lead to resistance, making future infections harder to treat. Always complete the prescribed course, even if symptoms improve.
Home remedies, such as warm compresses and steam inhalation, can provide relief from symptoms. These methods can complement medical treatments and enhance comfort during recovery. For example, applying a warm compress to the affected ear can help alleviate pain and promote drainage. Additionally, staying hydrated and using saline nasal sprays can help keep the Eustachian tubes clear.
- Can ear infections go away on their own? Yes, many ear infections, especially viral ones, can resolve without treatment.
- How can I prevent ear infections? Practice good hygiene, manage allergies, and avoid exposure to smoke and pollutants.
- When should I see a doctor? If symptoms persist for more than a few days or worsen, it’s important to seek medical advice.
Understanding Ear Infections
This article explores the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for ear infections, providing essential information for understanding and managing this common condition effectively.
Ear infections are more than just a nuisance; they can be a source of significant discomfort and distress. When bacteria or viruses invade the middle ear, they can cause an inflammatory response, leading to pain and a feeling of fullness. It's crucial to understand that not all ear infections are the same. There are primarily two types: acute otitis media, which is a sudden onset infection, and otitis media with effusion, where fluid remains in the ear after an infection has cleared. Understanding these distinctions can make a world of difference in treatment and recovery.
But why do ear infections happen in the first place? Well, think of your ear as a well-maintained garden. Just like a garden needs proper drainage to flourish, your ears rely on the Eustachian tubes to keep fluids flowing and prevent blockages. When these tubes become swollen or blocked due to allergies, colds, or sinus infections, fluid can accumulate in the middle ear, creating a breeding ground for bacteria and viruses. This is why ear infections are particularly common in children, whose Eustachian tubes are shorter and more horizontal, making it easier for germs to reach the middle ear.
To further illustrate the issue, here’s a simple table that outlines the types of ear infections and their characteristics:
| Type of Ear Infection | Description | Common Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Acute Otitis Media | Sudden onset infection with pain and fever | Colds, allergies, sinus infections |
| Otitis Media with Effusion | Fluid accumulation without infection | Post-infection fluid retention, allergies |
Understanding ear infections is not just about knowing the symptoms; it's also about recognizing the importance of early intervention. If left untreated, complications can arise, ranging from temporary hearing loss to more serious conditions like mastoiditis. So, if you or your child are experiencing symptoms, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Remember, taking care of your ears is just as important as any other aspect of your health!
Identifying the symptoms of ear infections is vital for timely intervention. Symptoms can vary by age and include pain, fever, and irritability in children, while adults may experience hearing loss and drainage.
Children often exhibit specific signs of ear infections, such as tugging at the ear, fussiness, and difficulty sleeping. Early detection is essential to prevent complications and ensure prompt treatment.
In adults, ear infections may manifest through ear pain, fluid drainage, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. Recognizing these symptoms can lead to quicker medical attention.
Understanding the causes of ear infections helps in prevention and management. Common triggers include allergies, colds, and sinus infections, which can lead to fluid buildup in the ear.
Allergies can cause inflammation in the nasal passages, leading to fluid accumulation in the ears. This fluid can become infected, resulting in an ear infection that requires medical attention.
Upper respiratory infections, such as colds or flu, are often precursors to ear infections. They can cause swelling and blockage of the Eustachian tubes, leading to fluid retention and infection.
Effective treatment for ear infections may include antibiotics, pain relievers, and home remedies. Understanding these options can help in choosing the best course of action for recovery.
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed for bacterial ear infections, while over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort. It's essential to follow medical advice for optimal recovery.
Home remedies, such as warm compresses and steam inhalation, can provide relief from symptoms. These methods can complement medical treatments and enhance comfort during recovery.
Q: Can ear infections be prevented?
A: While not all ear infections can be prevented, practicing good hygiene, avoiding exposure to smoke, and ensuring vaccinations are up to date can reduce the risk.
Q: How long do ear infections usually last?
A: Ear infections can vary in duration, but most resolve within a few days to a week with proper treatment.
Q: When should I see a doctor?
A: If you or your child experience severe pain, high fever, or symptoms that persist beyond a few days, it's time to seek medical advice.

Common Symptoms
Identifying the symptoms of ear infections is vital for timely intervention. These infections can present themselves in various ways, and recognizing these signs early can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. Symptoms often differ between children and adults, making it essential to understand how each group may react to this uncomfortable condition.
For children, the signs of an ear infection can be quite distinct. They may not always be able to articulate what they’re feeling, so parents should be vigilant for certain behaviors. Common symptoms in children include:
- Tugging at the ear: This is often a clear indication that something is bothering them.
- Increased fussiness: If your child is unusually irritable or crying more than usual, it could be a sign of discomfort.
- Difficulty sleeping: The pain from an ear infection can make it hard for children to settle down at night.
- Loss of appetite: Pain while swallowing or chewing can lead to a decrease in food intake.
In adults, the symptoms of ear infections can be more straightforward but equally distressing. Adults may notice:
- Ear pain: This is often a sharp, throbbing sensation that can be quite uncomfortable.
- Fluid drainage: Some adults may experience discharge from the ear, which can be a sign of infection.
- Feeling of fullness: A sensation of pressure or fullness in the ear can accompany the pain.
- Hearing loss: Temporary hearing difficulties can occur due to fluid buildup or inflammation.
Being aware of these symptoms can lead to quicker medical attention and better management of the condition. If you or your child are experiencing any of these signs, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. Remember, early detection not only alleviates discomfort but also helps prevent potential complications that can arise from untreated ear infections.
Here are some common questions regarding ear infections:
- What should I do if I suspect an ear infection? It's best to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
- Are ear infections contagious? No, ear infections themselves are not contagious, but the viruses or bacteria that cause them can be.
- Can ear infections lead to hearing loss? While most ear infections resolve without complications, untreated infections can lead to temporary or even permanent hearing loss.
Symptoms in Children
When it comes to identifying ear infections in children, parents often find themselves in a challenging situation. Kids, especially toddlers, can't always articulate what they’re feeling. Instead, they communicate their discomfort through behaviors that can be subtle or pronounced. One of the most common signs is tugging at the ear. When your little one keeps pulling or rubbing their ear, it’s often their way of saying, "Something's not right!"
Moreover, children may become increasingly fussy or irritable. If your usually cheerful child suddenly turns into a little ball of crankiness, it might be worth considering an ear infection as a potential culprit. Alongside this, difficulties sleeping can also arise. If your child is tossing and turning or waking up frequently during the night, it could be due to the discomfort caused by the infection. Ear pain can be especially bothersome when lying down, making it hard for them to settle.
In addition to these behavioral signs, physical symptoms can also manifest. Look out for fever, which can be a common response to infection. A mild fever may not be alarming, but if it spikes, it’s a good idea to consult a healthcare professional. Another symptom to watch for is fluid drainage from the ear. This can indicate that the infection is more severe and may require immediate medical attention. Lastly, if your child is experiencing a loss of appetite, it could be linked to the discomfort they feel when swallowing or chewing.
To summarize, here are some key symptoms to look for:
- Tugging or pulling at the ear
- Increased fussiness or irritability
- Difficulties sleeping
- Fever
- Fluid drainage from the ear
- Loss of appetite
Recognizing these symptoms early can make a significant difference in your child's comfort and recovery. If you suspect an ear infection, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Symptoms in Adults
When it comes to ear infections in adults, the symptoms can often be a bit more subtle than in children, yet they are just as important to recognize. Adults may experience a variety of discomforts that signal an ear infection, and understanding these symptoms can lead to quicker treatment and relief. One of the most common signs is a persistent earache, which can range from a dull ache to sharp pain that seems to come and go. This pain is often exacerbated by changes in pressure, such as during flights or when diving.
Another symptom that adults might notice is a sensation of fullness in the ear, as if it is clogged or blocked. This feeling can be quite bothersome and may accompany a noticeable decrease in hearing ability. In some cases, individuals might also experience fluid drainage from the ear, which can be alarming. This drainage can be clear, yellow, or even bloody, indicating the need for medical attention.
In addition to these physical symptoms, adults can also experience systemic signs like fever, which often accompanies infections. A low-grade fever might be present, signaling that the body is fighting off an infection. Furthermore, some adults report feeling fatigued or generally unwell, which can be attributed to the body's immune response to the infection. It’s important to listen to your body and seek medical advice if you notice these symptoms persisting.
To summarize, here are some key symptoms to watch for in adults experiencing ear infections:
- Ear pain: Ranges from dull to sharp.
- Feeling of fullness: A sensation that the ear is blocked.
- Hearing loss: Temporary decrease in hearing ability.
- Fluid drainage: May be clear, yellow, or bloody.
- Fever: Often low-grade.
- Fatigue: General feeling of being unwell.
Recognizing these symptoms early can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. If you find yourself experiencing any combination of these signs, don't hesitate to consult a healthcare provider. Remember, timely intervention is key to avoiding complications and ensuring a swift recovery.
Q: How can I tell if I have an ear infection?
A: Look for symptoms such as ear pain, a feeling of fullness, hearing loss, and any fluid drainage. If these symptoms persist, it's best to consult a doctor.
Q: Can ear infections go away on their own?
A: Some mild ear infections may resolve without treatment, but it's important to monitor symptoms. If they worsen or do not improve, seek medical attention.
Q: What should I do if I suspect an ear infection?
A: Schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.

Causes of Ear Infections
Understanding the causes of ear infections is crucial for both prevention and effective management. Ear infections primarily arise when bacteria or viruses invade the middle ear, leading to inflammation and discomfort. But what triggers this invasion? Several common factors can contribute to the development of ear infections, and being aware of these can help you take proactive steps to avoid them.
One of the most significant culprits behind ear infections is allergies. When allergens enter the body, they can cause inflammation in the nasal passages, which may lead to fluid accumulating in the ears. This fluid can become a breeding ground for bacteria, resulting in an infection that often requires medical intervention. Imagine your ears as a cozy little room; if the door is blocked (due to inflammation), the room can quickly fill with unwanted guests (bacteria), leading to a mess that needs to be cleaned up.
Another common cause is upper respiratory infections, such as colds or the flu. These infections can cause swelling and blockage of the Eustachian tubes, the channels that help equalize pressure in the ears. When these tubes become blocked, fluid can build up in the middle ear, creating an environment ripe for infection. Think of it like a traffic jam: when the roads are blocked, everything gets backed up, and the longer it lasts, the more chaos ensues.
In addition to allergies and respiratory infections, other factors can also contribute to ear infections:
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to smoke, pollution, or other irritants can increase the risk of ear infections.
- Age: Children are more susceptible to ear infections due to their shorter Eustachian tubes, which can easily become blocked.
- Seasonal Changes: Changes in weather can affect the incidence of colds and allergies, subsequently influencing ear infections.
Understanding these causes can empower you to take preventive measures. For instance, if you know that allergies trigger your ear infections, you might consider consulting an allergist or taking steps to minimize exposure to allergens. Similarly, practicing good hygiene during cold and flu season can help reduce your risk of developing upper respiratory infections that might lead to ear issues.
In summary, ear infections can stem from various sources, including allergies, respiratory infections, environmental factors, and age-related vulnerabilities. By recognizing these triggers, you can better manage your ear health and seek appropriate treatment when necessary.
Q: Can ear infections be prevented?
A: While not all ear infections can be prevented, practicing good hygiene, managing allergies, and avoiding exposure to smoke can help reduce the risk.
Q: How do I know if I have an ear infection?
A: Symptoms may include ear pain, fluid drainage, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. If you experience these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional.
Q: Are ear infections serious?
A: Most ear infections are not serious and can be treated effectively. However, recurrent infections may require further medical evaluation.
Allergies and Infections
Allergies can significantly contribute to the development of ear infections, creating a perfect storm for discomfort and pain. When allergens like pollen, dust mites, or pet dander invade our bodies, they trigger an immune response that leads to inflammation in the nasal passages. This inflammation can obstruct the Eustachian tubes, which are responsible for equalizing pressure in the ears and draining fluid. As a result, fluid can accumulate in the middle ear, creating an environment ripe for bacterial or viral growth. Imagine your ears as tiny balloon-like structures that need to stay inflated and clear; when allergies come into play, they can quickly become deflated and congested, leading to that annoying feeling of fullness.
Furthermore, the connection between allergies and ear infections is not just a one-way street. In fact, if you have a history of allergies, you're more likely to experience recurrent ear infections. This cycle can be frustrating, especially for children, who may not be able to articulate their discomfort. Parents should remain vigilant for signs of ear infections, particularly during allergy season when symptoms may flare up. Keeping track of allergy triggers and managing them effectively can help reduce the risk of ear infections.
In addition to allergies, respiratory infections like colds can also lead to ear infections. When you catch a cold, the congestion and mucus buildup can block the Eustachian tubes just like allergies do. This blockage can prevent fluid from draining properly, creating a breeding ground for bacteria. It's a vicious cycle: a cold leads to congestion, congestion leads to fluid buildup, and fluid buildup can lead to an ear infection. Understanding this relationship can empower individuals to take preventive measures, such as getting vaccinated against the flu or practicing good hygiene to minimize the risk of respiratory infections.
To summarize, allergies and infections are closely linked, and being proactive about managing allergies can significantly reduce the risk of developing ear infections. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Identify and Avoid Triggers: Keep a diary of allergy symptoms to pinpoint what exacerbates them.
- Consult a Doctor: Consider allergy testing to understand your sensitivities better.
- Use Medications Wisely: Over-the-counter antihistamines or nasal sprays can help alleviate allergy symptoms.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Regular hand washing can prevent the spread of respiratory infections.
By understanding the intricate relationship between allergies and ear infections, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their ear health and enjoy a more comfortable life.
1. Can allergies cause ear infections in adults?
Yes, adults can also experience ear infections as a result of allergies. The inflammation caused by allergies can lead to fluid buildup in the ears, increasing the risk of infection.
2. What are the signs of an ear infection?
Common signs of an ear infection include ear pain, fluid drainage, fever, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. In children, you might also notice fussiness or difficulty sleeping.
3. How can I prevent ear infections related to allergies?
To prevent ear infections, identify and avoid allergy triggers, use medications as recommended, and maintain good hygiene to reduce the risk of respiratory infections.
4. When should I see a doctor for an ear infection?
If you or your child experience severe ear pain, high fever, or symptoms that persist for more than a couple of days, it's important to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and treatment.
Respiratory Infections
Respiratory infections are more than just a common cold; they can be the gateway to various complications, including ear infections. When a person contracts a respiratory infection, such as the flu or a cold, the body responds by fighting off the invading pathogens, but this process can lead to inflammation and swelling in the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes. Imagine these tubes as tiny highways connecting your throat to your ears; when they become blocked due to swelling, fluid can accumulate in the middle ear, creating the perfect environment for bacteria or viruses to thrive.
In fact, studies have shown that children and adults alike who experience frequent upper respiratory infections are at a higher risk of developing ear infections. This correlation is particularly concerning for parents, as children are more susceptible to both respiratory and ear infections due to their still-developing immune systems. As a parent, it’s essential to be vigilant about your child’s health during cold and flu season. If you notice symptoms such as persistent ear tugging or unusual fussiness after your child has had a cold, it may be time to consult a healthcare professional.
Moreover, the common cold can lead to a range of symptoms that might not seem directly related to ear infections but are crucial to understanding the bigger picture. Some of these symptoms include:
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Sore throat
- Coughing
- Fever
When these symptoms are present, it’s a clear indication that the body is fighting off an infection. However, if left untreated, the congestion and inflammation can lead to a buildup of fluid in the ear, increasing the risk of developing an ear infection. It’s a cycle that can be difficult to break, especially during peak seasons for respiratory illnesses.
Understanding this relationship between respiratory infections and ear infections is crucial for prevention. Maintaining good hygiene, such as frequent hand washing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals, can significantly reduce the risk of contracting respiratory infections. Additionally, ensuring that children are up to date on vaccinations can also help in preventing illnesses that lead to ear infections. In summary, being proactive about respiratory health can have a direct impact on ear health, making it essential to pay attention to the signs and symptoms that may arise during cold and flu season.
Q: What are the signs that my child might have an ear infection after a cold?
A: Look for symptoms such as tugging at the ear, increased irritability, difficulty sleeping, or fluid drainage from the ear. If these persist, consult a healthcare provider.
Q: Can adults get ear infections from respiratory infections?
A: Yes, adults can also develop ear infections as a result of upper respiratory infections, often experiencing symptoms like ear pain, a feeling of fullness, or fluid drainage.
Q: How can I prevent ear infections in my children?
A: Good hygiene practices, staying current on vaccinations, and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke can help reduce the risk of ear infections.

Treatment Options
When it comes to treating ear infections, understanding your options is crucial for a swift recovery. Ear infections can be bothersome and painful, but fear not! There are several effective treatment methods available to help alleviate symptoms and tackle the infection head-on. The primary treatment options generally fall into two categories: medications and home remedies. Each has its unique benefits and can be tailored to suit individual needs.
First up, we have antibiotics, which are often the go-to solution for bacterial ear infections. These medications work by targeting the bacteria causing the infection, helping to reduce inflammation and eliminate the source of pain. However, it's essential to remember that antibiotics are not effective against viral infections, which can sometimes mimic the symptoms of an ear infection. Therefore, a proper diagnosis from a healthcare professional is vital before starting any medication.
In addition to antibiotics, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be incredibly helpful in managing discomfort associated with ear infections. These medications not only help alleviate pain but can also reduce fever, making you feel much more comfortable during the healing process. Always follow the recommended dosage on the packaging or consult with a healthcare provider if you're unsure.
Now, while medications play a significant role in treatment, don't overlook the power of home remedies. Many people find relief through simple, natural methods that can complement medical treatments. For instance, applying a warm compress to the affected ear can soothe pain and provide a sense of comfort. The warmth helps to increase blood flow to the area, promoting healing and easing discomfort. Another popular remedy is steam inhalation, which can help clear up congestion and promote drainage from the ears, reducing pressure and discomfort.
For those interested in a more holistic approach, here’s a quick overview of some effective home remedies:
- Warm Compress: Apply a warm cloth or heating pad to the ear for 20 minutes.
- Steam Inhalation: Inhale steam from a bowl of hot water to help relieve congestion.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids helps thin mucus and promotes drainage.
- Elevation: Keeping your head elevated can help fluid drain from the ear.
Before starting any treatment, it's always wise to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if symptoms persist or worsen. They can provide personalized advice and determine whether further intervention is necessary, such as a referral to an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist. Remember, being proactive about your health is the best way to ensure a speedy recovery from ear infections.
1. Can ear infections go away on their own?
Yes, many ear infections, especially viral ones, can resolve without treatment. However, if symptoms persist, it's essential to seek medical advice.
2. How can I prevent ear infections?
Preventative measures include keeping the ears dry, avoiding smoke exposure, and managing allergies effectively.
3. When should I see a doctor for an ear infection?
If you experience severe pain, fever, hearing loss, or if symptoms last more than a couple of days, consult a healthcare professional.
4. Are there any long-term effects of ear infections?
While most ear infections resolve without complications, recurrent infections can lead to hearing loss or other issues, so timely treatment is crucial.
Antibiotics and Medications
When it comes to treating ear infections, antibiotics play a crucial role, especially when the infection is caused by bacteria. These medications work by targeting the bacteria responsible for the infection, helping to alleviate symptoms and speed up recovery. It’s important to note that not all ear infections require antibiotics; in fact, many are viral in nature, and antibiotics won’t be effective against them. This is why it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis before starting any treatment.
For bacterial ear infections, your doctor may prescribe a specific antibiotic based on the type of bacteria suspected or confirmed. Common antibiotics for ear infections include:
| Antibiotic | Typical Dosage | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | 500 mg every 8 hours | Nausea, diarrhea |
| Augmentin | 875 mg every 12 hours | Stomach upset, skin rash |
| Cefdinir | 300 mg every 12 hours | Diarrhea, headache |
In addition to antibiotics, over-the-counter medications can help manage the discomfort associated with ear infections. Pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can reduce fever and alleviate pain, making it easier for both children and adults to cope with the symptoms. Always follow the recommended dosages on the packaging or as advised by your healthcare provider to ensure safe usage.
It’s also essential to stay hydrated and rest your body during recovery. Some people find relief from symptoms through home remedies, such as applying a warm compress to the affected ear or using steam inhalation to ease pressure and discomfort. While these methods can provide some comfort, they should not replace prescribed medications. Always discuss any home remedies with your doctor to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your situation.
In summary, while antibiotics are vital for treating bacterial ear infections, understanding when and how to use them is equally important. Combining medical treatments with supportive care can enhance recovery and improve overall comfort. Remember, if symptoms persist or worsen, seeking medical attention is crucial to avoid complications.
- Can ear infections go away on their own? Yes, many ear infections, especially viral ones, can resolve without antibiotics. However, monitoring symptoms is essential.
- How long does it take for antibiotics to work? Antibiotics typically start to show improvement within 48-72 hours, but it’s important to complete the full course as prescribed.
- Are there any risks associated with taking antibiotics? Yes, potential side effects can include allergic reactions, gastrointestinal issues, and the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
Home Remedies
When it comes to managing ear infections, many people look for that can provide relief and complement medical treatments. While it's essential to follow your doctor's advice, incorporating some simple, natural methods can help ease discomfort. One of the most popular remedies is the use of warm compresses. Applying a warm cloth to the affected ear can help reduce pain and promote drainage by increasing blood flow to the area. This method is particularly effective for children who may be hesitant to take medication.
Another effective home remedy is steam inhalation. Breathing in steam can help relieve congestion and facilitate the drainage of fluid from the ear. You can achieve this by taking a hot shower or using a bowl of hot water. Just be sure to cover your head with a towel to trap the steam and breathe deeply. This method not only helps with ear infections but can also alleviate symptoms of colds and sinus infections, which are often related.
Additionally, staying hydrated is crucial. Drinking plenty of fluids helps thin mucus and promotes drainage, reducing the risk of further infection. Herbal teas, especially those containing ingredients like ginger or chamomile, can be soothing and beneficial. You might also consider using essential oils such as tea tree oil or lavender oil, which have natural antibacterial properties. Diluting these oils with a carrier oil and applying them around the ear (not inside) may provide additional relief.
It's important to note that while home remedies can be effective, they should not replace professional medical advice. If symptoms persist or worsen, seeking medical attention is crucial. Remember, every individual's situation is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Always consult with a healthcare provider to ensure you're taking the right approach for your condition.
- Can ear infections be treated at home?
Yes, some home remedies can provide relief, but it's essential to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. - How long do ear infections typically last?
Ear infections can last from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on the severity and treatment. - When should I see a doctor for an ear infection?
If symptoms persist for more than a couple of days, worsen, or if you experience severe pain, it's important to seek medical attention. - Are there any preventive measures for ear infections?
Yes, practicing good hygiene, avoiding smoking, and managing allergies can help reduce the risk of ear infections.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the main symptoms of an ear infection?
The symptoms of an ear infection can vary depending on the age of the individual. In children, common signs include tugging at the ear, fussiness, difficulty sleeping, and sometimes fever. Adults may experience ear pain, a feeling of fullness in the ear, fluid drainage, and even temporary hearing loss. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to timely treatment.
- What causes ear infections?
Ear infections are typically caused by bacteria or viruses that invade the middle ear. Common triggers include upper respiratory infections like colds and flu, allergies that lead to inflammation in the nasal passages, and sinus infections that can cause fluid buildup in the ear. Understanding these causes can help in preventing future infections.
- How are ear infections treated?
Treatment for ear infections often depends on whether the infection is bacterial or viral. For bacterial infections, antibiotics are usually prescribed. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort. Additionally, home remedies such as warm compresses and steam inhalation can provide relief and complement medical treatments.
- Are ear infections contagious?
No, ear infections themselves are not contagious. However, the respiratory infections that can lead to ear infections, such as colds and flu, can be contagious. It's important to practice good hygiene to prevent the spread of these underlying infections.
- When should I see a doctor for an ear infection?
If you or your child experience severe ear pain, fever, or symptoms that last longer than a couple of days, it's wise to consult a healthcare professional. Early intervention can prevent complications and ensure appropriate treatment.
- Can ear infections lead to complications?
Yes, if left untreated, ear infections can lead to complications such as hearing loss, the spread of infection to nearby structures, or even the development of chronic ear problems. This is why recognizing symptoms early and seeking treatment is crucial.
- Are there any home remedies for ear infections?
Yes, some effective home remedies include applying a warm compress to the affected ear, using steam inhalation to relieve congestion, and staying hydrated. However, these should be used in conjunction with medical advice and not as a substitute for professional treatment.